In industries ranging from pharmaceuticals and chemicals to printing and coatings, solvents are indispensable. However, their widespread use comes with significant costs—both financial and environmental. Disposing of solvents as hazardous waste is expensive, and improper handling can lead to regulatory penalties or ecological harm. This is where solvent recovery emerges as a game-changing solution.
If you’re exploring solvent recovery options, you likely have questions: How does solvent recovery work? What are the steps involved? Why invest in a solvent recovery machine? This article dives deep into the processes, benefits, and innovations in solvent recovery technology, empowering you to make informed decisions for your business.

Why Solvent Recovery Matters: The Problem with Traditional Disposal
Before explaining the how, let’s address the why. Solvents like acetone, ethanol, toluene, and methanol are costly to purchase and even costlier to dispose of. Regulatory bodies classify many solvents as hazardous waste, requiring specialized disposal methods. For businesses generating large volumes of solvent waste, disposal fees can cripple profitability. Worse, single-use solvents contribute to environmental pollution and resource depletion.
The solution? Reclaim and reuse solvents through recovery. This not only slashes costs but also aligns with global sustainability goals. Modern solvent recovery machines make this process efficient, safe, and scalable.
The Solvent Recovery Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Solvent recovery involves separating contaminants from used solvents to restore them to a reusable state. While methods vary depending on the solvent type and contamination level, the core process typically follows these stages:
1. Collection and Pre-Treatment
Used solvents are collected in dedicated containers to avoid cross-contamination. Pre-treatment may include filtration to remove solid particles (e.g., paint residues, metal shavings) or centrifugation for sludge separation. This step ensures the solvent is ready for distillation.
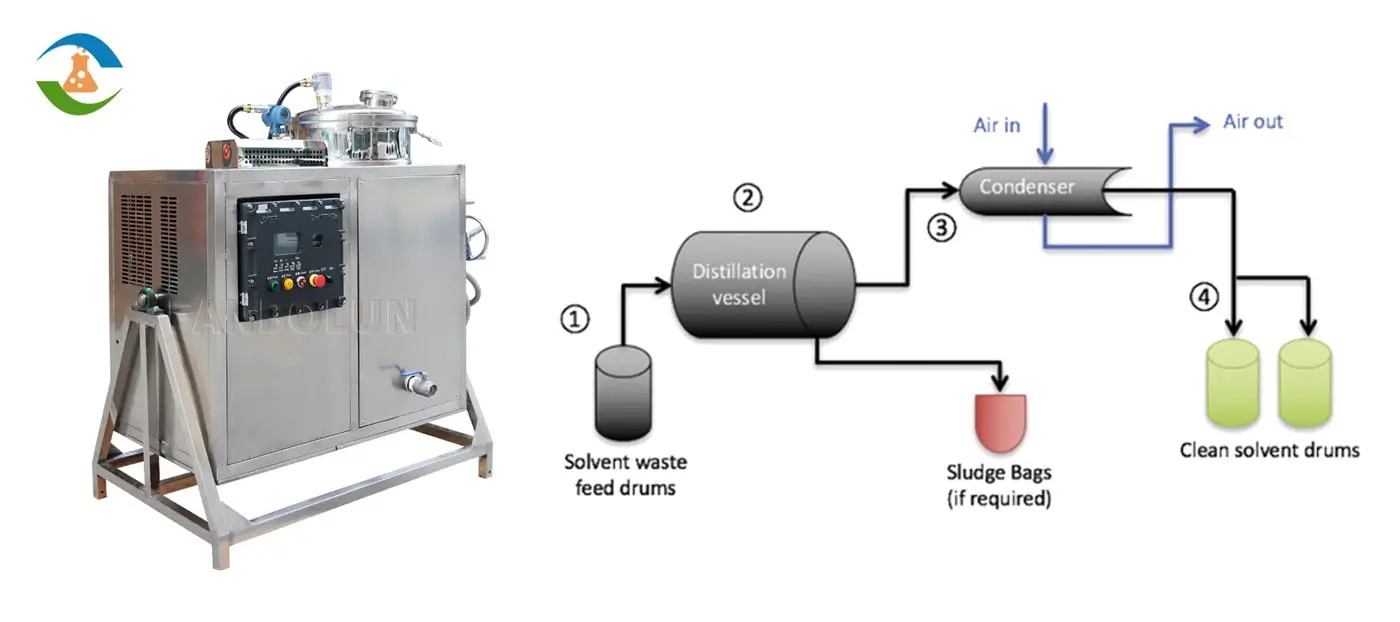
2. Distillation: The Heart of Recovery
Distillation is the most common and effective method for solvent recovery. It exploits differences in boiling points to separate solvents from contaminants. Here’s how it works:
Heating: The contaminated solvent is heated in a closed vessel. As temperatures rise, the solvent (with a lower boiling point) vaporizes first.
Vaporization and Condensation: The solvent vapor is directed to a condenser, where it cools and returns to liquid form.
Separation: Purified solvent is collected in a clean tank, while non-volatile contaminants (e.g., oils, polymers) remain as residue.
Advanced solvent recovery machines automate this process, ensuring precision and repeatability.
3. Post-Treatment and Quality Testing
Recovered solvents undergo quality checks to verify purity levels. Techniques like gas chromatography (GC) or refractive index analysis may be used. If needed, additional treatments—such as activated carbon filtration—remove trace impurities.
4. Reuse or Storage
Once certified, the solvent is either reused immediately in production or stored for future use. High-quality recovery can restore solvents to 90–95% purity, matching virgin-grade performance.
Traditional vs. Modern Solvent Recovery: Why Machines Outperform Manual Methods
Historically, companies relied on manual distillation setups or outsourced recovery to third parties. However, these approaches have critical drawbacks:
Manual Systems: Labor-intensive, inconsistent, and prone to safety risks (e.g., overheating, leaks).
Outsourcing: High transportation and service fees, delayed turnaround times, and loss of control over quality.
Modern solvent recovery machines eliminate these issues by offering:
Automation: Programmable controls for temperature, pressure, and cycle times.
Energy Efficiency: Advanced heat recovery systems reduce energy consumption by up to 50%.
Safety Features: Explosion-proof designs, automatic shutoff, and leak detection.
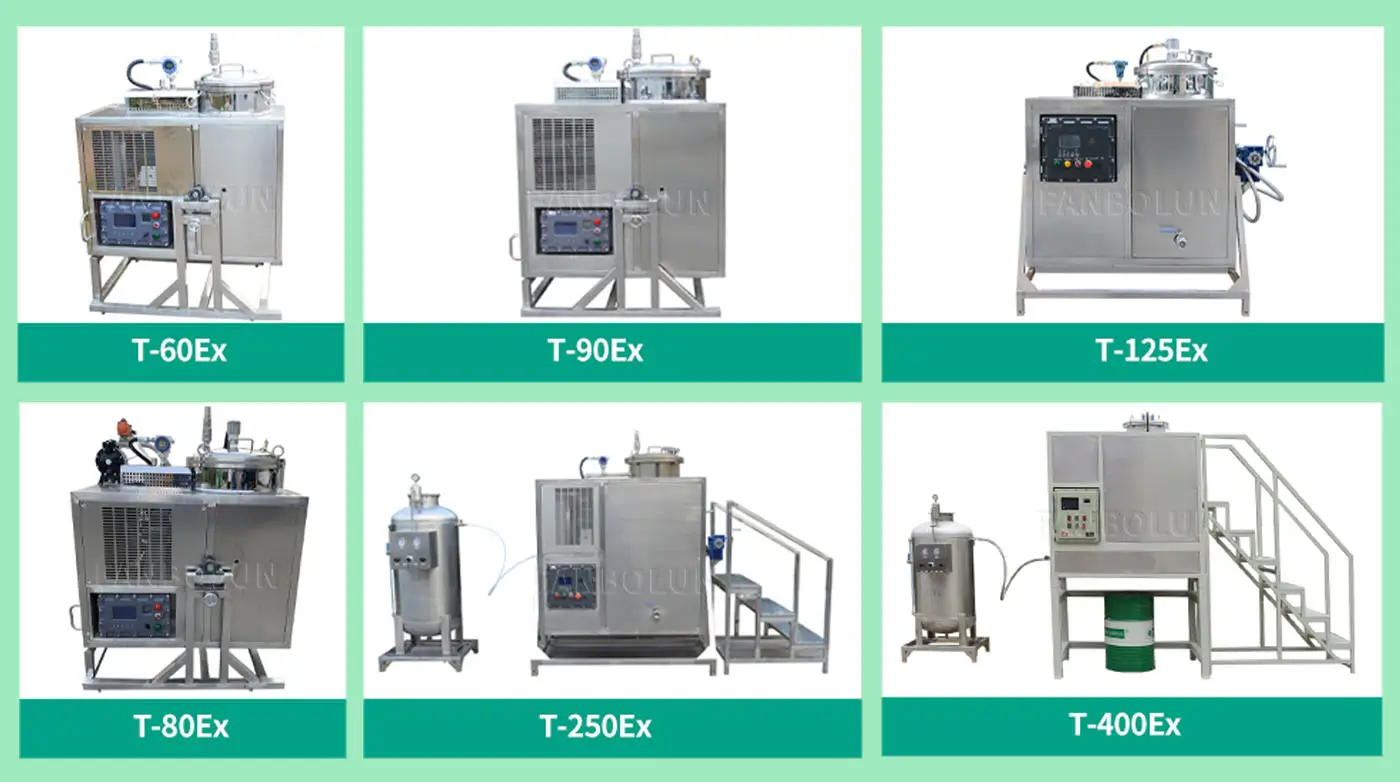
Scalability: Machines are available in sizes from benchtop units (for labs) to industrial-scale systems.
For example, a pharmaceutical company using a solvent recycler machine could reclaim 10,000 liters of acetone annually, saving over $50,000 in procurement costs while reducing carbon emissions.

Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Solvent Recovery Machine
Not all solvents or industries have the same needs. Here’s what to evaluate when selecting equipment:
Solvent Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle your solvent’s boiling point, corrosiveness, and flammability.
Capacity: Match the machine’s throughput (liters/hour) to your waste volume.
Purity Requirements: Industries like electronics or pharmaceuticals demand ultra-high purity (≥99%), while others may tolerate 90–95%.
Regulatory Compliance: Look for certifications (e.g., ATEX for explosive environments) and emissions control systems.
Ease of Maintenance: Self-cleaning functions and accessible parts reduce downtime.
Industries That Benefit Most from Solvent Recovery Machines
Chemical Manufacturing: Recover acetone, THF, or DMF from reactions.
Pharmaceuticals: Reclaim methanol or ethanol used in drug synthesis.
Paint and Coatings: Reuse solvents like xylene or ethyl acetate.
Printing: Recycle inks and cleaning solvents.
Automotive: Recover degreasers and parts-cleaning agents.


Environmental and Economic Benefits: By the Numbers
Cost Savings: Recovering 1 liter of solvent costs 30–70% less than buying new. For a mid-sized factory, annual savings can exceed $200,000.
Waste Reduction: Cut hazardous waste generation by up to 90%.
Carbon Footprint: Recycling solvents uses 60% less energy than producing virgin solvents.
Regulatory Compliance: Avoid fines and enhance ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting.
Why Partner with a Professional Solvent Recovery Machine Manufacturer?
As a global manufacturer specializing in solvent recovery systems, we understand the unique challenges faced by industries worldwide. Our machines are engineered for:
Durability: Stainless steel construction resistant to corrosion.
Smart Controls: IoT-enabled monitoring and data logging.
Customization: Tailored solutions for niche solvents or high-volume needs.
Global Support: Installation, training, and maintenance services.

Conclusion: Future-Proof Your Business with Solvent Recovery
Solvent recovery isn’t just a cost-saving measure—it’s a strategic investment in sustainability and operational efficiency. By adopting advanced recovery technology, businesses can turn waste into value, comply with tightening regulations, and build a greener brand reputation.
Ready to explore solvent recovery machines tailored to your needs? [Contact us today] for a free consultation and discover how our solutions can transform your waste management strategy. Let’s reclaim your solvents—and your competitive edge—together.
