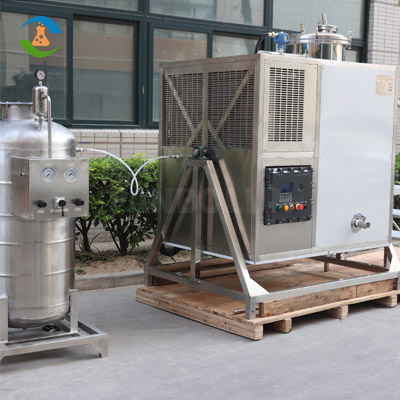
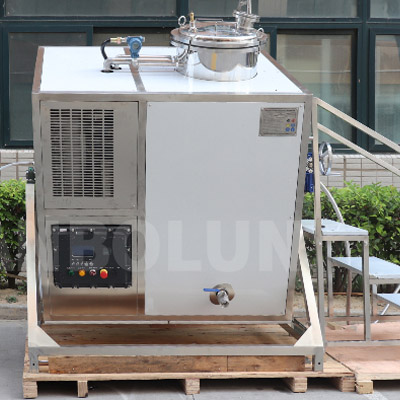
In today's world, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a crucial component of business strategy and operations. As industries evolve, there is a growing emphasis on adopting practices that not only benefit the environment but also enhance economic viability. One such practice is solvent recycling, a pivotal element in advancing the circular economy.
Understanding the Circular Economy
The circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources. This regenerative approach contrasts with the traditional linear economy, which follows a 'take, make, dispose' model. In a circular economy, the goal is to keep products, equipment, and infrastructure in use for longer, thus improving the productivity of these resources. This model relies heavily on recycling, reusing, and refurbishing materials to create a closed-loop system.

What is Solvent Recycling?
Solvent recycling is the process of reclaiming spent solvents from industrial processes and purifying them for reuse. Solvents are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and manufacturing, for cleaning, extraction, and other applications. Over time, solvents can become contaminated with impurities, reducing their effectiveness. Instead of disposing of these spent solvents, recycling allows companies to clean and reuse them, reducing the need for new solvent production.
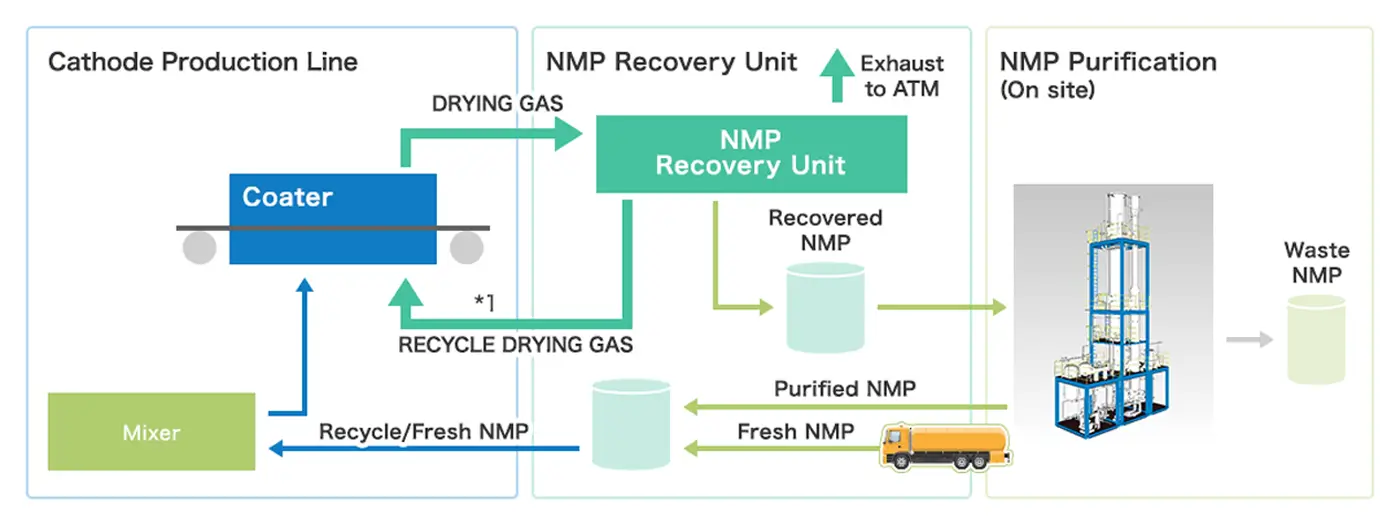
Solvent Recovery Diagram(NMP)
The Environmental Benefits of Solvent Recycling
Reducing Waste and Pollution
One of the primary environmental benefits of solvent recycling is the significant reduction in waste. By recycling solvents, companies can minimize the volume of hazardous waste generated, which in turn decreases the environmental burden associated with waste disposal. Proper solvent recycling prevents contaminated solvents from being discarded into landfills or water bodies, thus protecting soil and water quality.
Did you know that improper disposal of solvents can lead to severe soil and water contamination? The chemicals in solvents can seep into the ground and water sources, posing serious environmental and health risks. By implementing solvent recycling practices, industries can play a crucial role in mitigating these risks and safeguarding natural resources.
Conserving Natural Resources
Recycling solvents also conserves natural resources. The production of new solvents requires the extraction and processing of raw materials, which often involves significant energy consumption and environmental degradation. By recycling solvents, the demand for new raw materials decreases, leading to conservation of natural resources and reduction in environmental impact.
Economic Advantages of Solvent Recycling
Cost Savings
From a financial perspective, solvent recycling offers substantial cost savings. The cost of purchasing new solvents can be high, especially for industries that require large volumes. Recycling solvents can reduce the need for new purchases, thereby lowering operating costs. Additionally, many regions impose strict regulations on the disposal of hazardous waste, and non-compliance can result in hefty fines. By recycling solvents, companies can avoid these fines and reduce waste management costs.
Ever wondered how much money can be saved through solvent recycling? Depending on the scale of operations and the efficiency of the recycling process, companies can save thousands to millions of dollars annually. These savings can be reinvested into other areas of the business, fostering growth and innovation.

Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Solvent recycling also enhances operational efficiency. With a reliable solvent recycling system in place, companies can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality solvents, reducing downtime and improving productivity. This reliability is especially critical in industries where solvent purity directly impacts product quality and safety.
How Businesses Can Implement Solvent Recycling
Implementing solvent recycling in a business setting involves several key steps. While the process may seem complex, breaking it down into manageable phases can help ensure a smooth transition and successful integration into existing operations.
Assessing Current Solvent Use
The first step in implementing solvent recycling is to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the current solvent use within the organization. This includes identifying the types of solvents used, the volumes consumed, and the processes that generate spent solvents. Understanding these details is crucial for designing an effective recycling system tailored to the specific needs of the business.
Have you ever thought about how much solvent your business uses on a daily basis? By keeping track of solvent consumption and waste generation, companies can identify key areas where recycling can be most beneficial and impactful.
Selecting the Right Recycling Technology
Once the assessment is complete, the next step is to select the appropriate recycling technology. Various technologies, such as distillation, filtration, and adsorption, are available for solvent recycling. The choice of technology depends on the types of solvents being recycled, the level of contamination, and the desired purity of the recycled solvents.
Collaboration with technology providers and industry experts can help businesses choose the best recycling system. Additionally, pilot testing different technologies can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness and efficiency, ensuring that the selected system meets the company's requirements.

Solvent Recycling Equipment (90L)
Model: T-90EX
Feed capacity(L): 90
Power(kW): 5
Recovery(%): 95
View More
Solvent Recycler Machine (125L)
Model: T-125EX
Feed capacity(L): 125
Power(kW): 6
Recovery(%): 95
View More
Solvent Recycling Machine (250L)
Model: T-250EX
Feed capacity(L): 250
Power(kW): 16
Recovery(%): 95
View More
Solvent Recycling System (600L)
Model: T-600EX
Feed capacity(L): 600
Power(kW): 32
Recovery(%): 95
View More
Designing the Recycling System
Designing a solvent recycling system involves planning the layout, integrating it with existing processes, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. The system should be designed to handle the expected volumes of spent solvents and produce recycled solvents of the required quality. Key considerations include the capacity of the recycling equipment, the ease of operation, and the maintenance requirements.
How can businesses ensure that their solvent recycling system is efficient and compliant with regulations? Working closely with engineers, environmental consultants, and regulatory bodies can help design a system that is both effective and compliant with all necessary standards.
The Future of Solvent Recycling in the Circular Economy
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the role of solvent recycling in the circular economy is set to grow. With increasing regulatory pressure and consumer demand for environmentally friendly practices, more companies are likely to adopt solvent recycling. This shift will not only drive environmental benefits but also create economic opportunities and promote innovation.
Solvent recycling is a vital component of the circular economy. It reduces waste, conserves natural resources, and offers significant economic advantages. By embracing solvent recycling, companies can contribute to a more sustainable future while enhancing their operational efficiency and profitability. The path to sustainability is a journey, and solvent recycling is a crucial step in the right direction.