Industrial Wash Water Recycling: A Smart Step Toward Sustainable Manufacturing
Discover how recycling wash water and solvents can transform industrial operations, reduce costs, and protect the environment.
Learn More80% Water Reduction
Lower consumption with recycling systems
ROI in 18-24 Months
Recover your investment quickly
70% Lower Footprint
Reduce environmental impact
95% Solvent Recovery
Efficient recycling technology
What Is Industrial Wash Water Recycling?
Industrial wash water recycling refers to the process of cleaning, treating, and reusing wash water generated during manufacturing, cleaning, or maintenance operations. Instead of discharging contaminated water into the environment, industries can recover and reuse it, significantly reducing water consumption and waste disposal costs.
According to a 2023 report by the World Resources Institute, global industrial water demand is expected to increase by 50% by 2050. This makes water recycling technologies not just beneficial but essential for sustainable growth.
Why Is Recycling Wash Water Important?
Industrial facilities often use large volumes of water for cleaning machinery, parts, and surfaces. This water becomes contaminated with oils, solvents, and chemicals that can harm the environment if not properly treated. Recycling wash water allows industries to comply with environmental regulations while saving operational costs.
The Role of Solvent Recycler Machines
Many industries, especially those using solvents for cleaning or production, can integrate solvent recycler machines to recover solvents from wash water or waste mixtures. These machines use distillation or vacuum evaporation to separate usable solvents from contaminants.
For instance, a solvent recycling system can reclaim up to 95% of used solvents, allowing businesses to reuse them multiple times. This not only reduces chemical purchases but also minimizes hazardous waste disposal.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Recycling wash water and solvents contributes to both environmental protection and cost efficiency. Here are the main benefits:
Reduced water consumption: Less dependency on freshwater sources
Lower waste disposal costs: Decreased volume of hazardous waste
Regulatory compliance: Easier adherence to environmental standards
Operational savings: Reuse of solvents and water reduces raw material costs
Sustainability leadership: Improved corporate environmental responsibility
Community goodwill: Positive brand perception as an eco-friendly company
A report from the International Water Association (IWA) revealed that industries adopting closed-loop water recycling systems cut their overall water footprint by up to 70%.
Ready to Transform Your Water Management?
Explore our solvent recycling solutions tailored for your industry needs
Request a ConsultationApplications Across Industries
Industrial wash water recycling is applicable in various sectors including automotive, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and metal finishing. For example, car wash facilities already use car wash water recycling systems to minimize water waste and comply with environmental regulations.
Future Outlook: Smart Recycling and Data Integration
The future of industrial wash water recycling lies in automation and data analytics. Smart recycling systems equipped with sensors and AI can monitor water quality, predict maintenance needs, and optimize energy consumption in real time. According to a study by the International Energy Agency (IEA), integrating AI-driven monitoring systems can improve recycling efficiency by up to 25%.
As sustainability becomes a global priority, industries that adopt such technologies will not only reduce their environmental impact but also gain a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Industrial wash water recycling is more than a compliance measure—it's a strategic investment in sustainability and efficiency. By implementing solvent recycling systems and water reuse technologies, industries can significantly lower costs, conserve resources, and contribute to a cleaner planet.
For businesses looking to start, exploring advanced solvent recovery systems is an excellent first step toward sustainable industrial operations.
Industry Case Studies
Automotive
Automobile manufacturers reduce water consumption by 75% using closed-loop systems.
Read Case StudyPharmaceutical
Recovering 98% of solvents while maintaining strict quality standards.
Read Case StudyMetal Finishing
Recycling systems cut water costs by 60% while meeting EPA requirements.
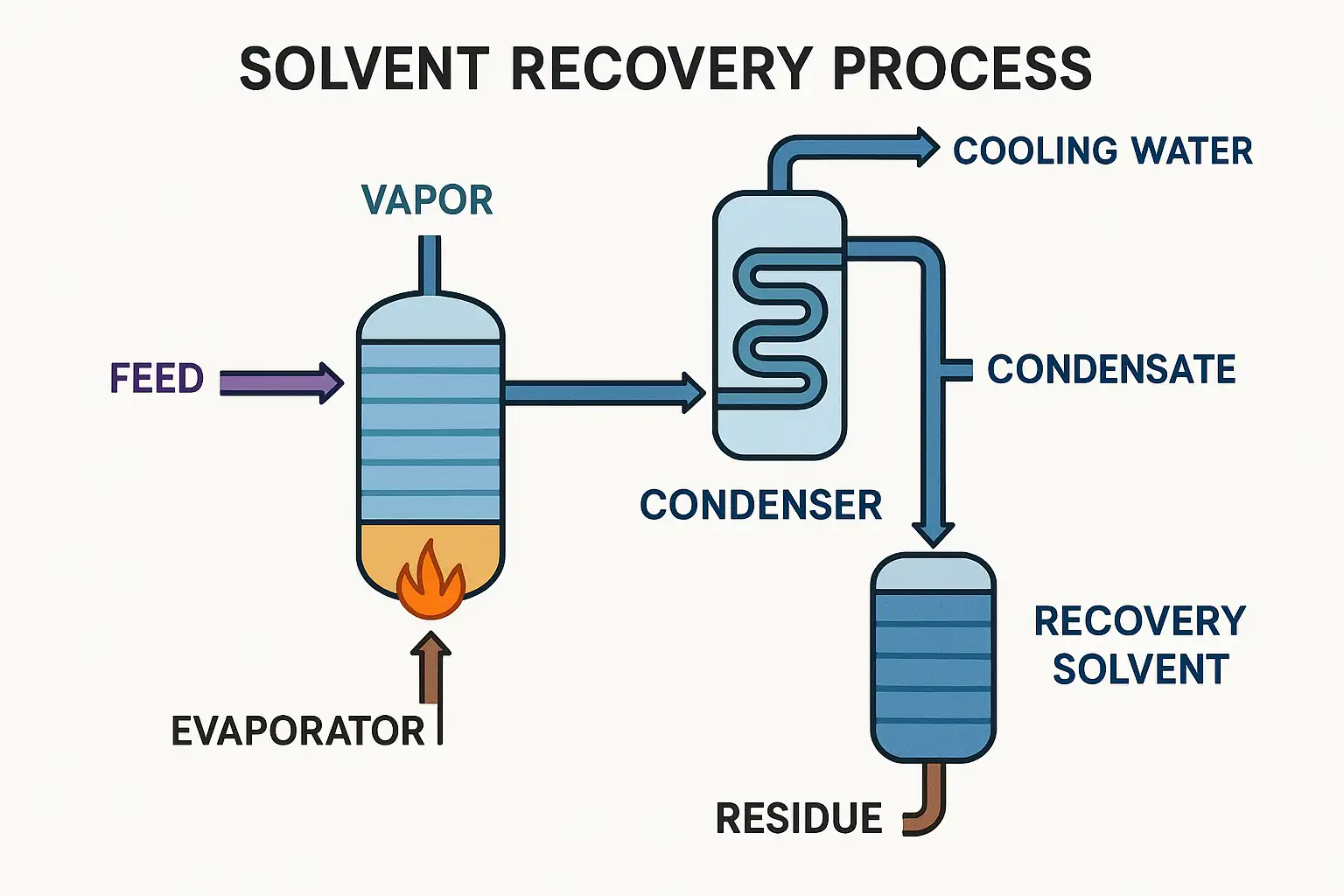
Read Case StudyHow Solvent Recycling Works
Most solvent recovery systems use distillation methods to separate solvents from contaminants:
Contaminated Solvent Input: Waste solvents enter the system
Heating: Solution heated to specific boiling points
Vapor Separatio Contaminants separate from solvent vapor
Condensation: Clean solvent vapor condenses into liquid
Pure Solvent Output: Ready-to-reuse solvent collected
Learn how solvent recycling systems can benefit your operation.