Solvent Recovery Distillation Unit: A Practical Guide for Real-World Plants
Learn how solvent recovery distillation units drastically reduce solvent costs and waste for industrial facilities. Keyword focus: solvent recovery distillation unit, solvent recycler machine, solvent recycling system.
What Is a Solvent Recovery Distillation Unit?
A solvent recovery distillation unit is equipment that heats dirty solvent, evaporates it, and condenses it back into clean, reusable solvent. Instead of paying to buy fresh solvent and dispose of used solvent, the same liquid is reused again and again.

Why Solvent Recovery Matters Now
Many factories still treat solvent as a "consume and throw away" material. That approach is becoming more expensive each year.
Chemical costs are rising. Solvents account for 15-30% of variable production cost in coatings, printing and electronics manufacturing.
Disposal regulations tighten. In the US and EU, hazardous solvent waste disposal fees have increased over 20% in the last decade per industry surveys.
ESG scrutiny increases. Environmental reports now track VOC emissions, hazardous waste generation, and recycling rates.
Every liter recovered saves money, reduces risk, and boosts sustainability scores without compromising quality.
Does a solvent recovery unit only make sense for large factories?
Not at all. Modern units with capacities starting at 20L are widely used in small paint shops, labs, and workshops. A medium-size facility generating 40-60L of solvent waste per week sees typical ROI in 12-24 months. Learn about effective solvent disposal solutions for facilities of all sizes.
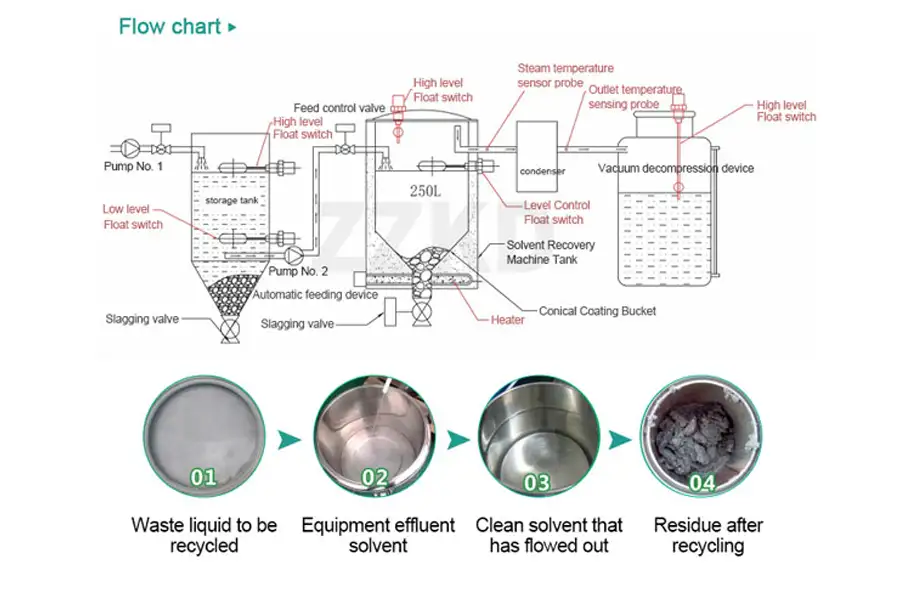
How a Solvent Recovery Distillation Unit Works
Although designs vary, most industrial units follow these essential steps:
Load: Contaminated solvent is poured or pumped into the distillation tank
Heat: The tank heats the solvent below contaminants' boiling points
Evaporate: Clean solvent vapor rises while residues stay in the boiler
Condense: Vapor cools through condensers and becomes liquid
Collect: Distilled solvent flows into clean containers for reuse
Discharge: Leftover residues (5-20% volume) are handled as hazardous waste
For technical details on solvent recovery system operation, see our comprehensive industry-specific explainer.
Capacity Ranges: From 20L to 400L
Below are specifications from a family of explosion-proof solvent recovery distillation units. Values vary by manufacturer but represent industrial norm ranges.
| Model | Capacity (L) | Power (kW) | Temp Range (°C) | Process Time (min) | Recovery (%) | Weight (kg) | Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-20Ex | 20 | 2 | RT–200 | 120 | 95 | 153 | 860×760×1190 |
| T-60Ex | 60 | 4 | RT–200 | 150 | 95 | 170 | 1160×870×1260 |
| T-80Ex | 80 | 5 | RT–200 | 180 | 95 | 200 | 1180×850×1290 |
| T-125Ex | 125 | 6 | RT–200 | 210 | 95 | 280 | 1250×920×1450 |
| T-250Ex | 250 | 16 | RT–200 | 240 | 95 | 520 | 2600×1200×1950 |
| T-400Ex | 400 | 32 | RT–200 | 270 | 95 | 1200 | 1990×1850×2090 |
Recovery rates around 95% are standard for many organic solvents when operated correctly.
Is shorter treatment time always better?
Not necessarily. Very fast cycles may leave solvent partially contaminated or increase energy consumption. Optimized cycles balance: purity requirements, energy efficiency, and residue characteristics. Many plants achieve better cost-per-liter with slightly longer, carefully controlled cycles.
Key Benefits of Industrial Solvent Recovery
1. Significant Cost Savings
Every liter of recovered solvent is one liter that doesn't necessitate purchase, while simultaneously reducing waste disposal expenses.
Reduce solvent purchases. Facilities report 50-90% reductions after implementing properly sized units
Minimize hazardous waste. Only concentrated residues (typically 5-20% of original volume) require disposal
Fast ROI. Published case studies typically show payback within 1-3 years
2. Enhanced Safety & Compliance
U.S. EPA and ECHA actively promote solvent minimization and on-site treatment in official guidance documents.
Lower hazardous waste classification/reporting volumes
Reduced transportation of flammable liquids off-site
Superior VOC emission control through closed systems
3. Sustainability & ESG Impacts
Corporate sustainability reports increasingly track:
Hazardous waste per production unit
Percentage of recycled raw materials
Scope 3 emissions from waste transport/treatment
Implementing solvent recycling systems improves all key environmental metrics for ESG reporting.
Selecting the Right Solvent Recycler
Selection prioritizes matching technology to specific solvent streams rather than "bigger is better" approach.
1. Analyze Solvent Composition
Boiling points: Lower-boiling solvents (acetone, IPA) require less energy than high-boilers
Residue type: Paints, inks and resins affect cleaning procedures and automation options
Contaminants: Acids/reactive chemicals require special materials like 316 stainless steel
2. Determine Your Volume Requirements
Simple calculation method:
Estimate average solvent waste per day/shift
Determine available daily operation hours (single shift, 24hr, etc.)
Divide total volume by practical batch size (60-125L)
This identifies batches required and optimal machine sizing.
3. Safety & Certification Essentials
Flammable solvents require ATEX, IECEx or local explosion-proof standards:
Over-temperature/pressure protection systems
Anti-static design with proper grounding
Adequate ventilation and gas detection

4. Operational Cost Factors
Total cost per liter includes:
Energy consumption per batch (electrical, steam)
Annual maintenance requirements
Operator time/automation levels needed
When is a fully automatic system worth the investment?
Automatic systems excel in high-volume continuous operations or when labor is constrained. For small-to-medium volumes (under 200L/day), semi-automatic units often provide optimal cost flexibility. Waste-stream mapping over several weeks reveals the most efficient approach.
Key Operational Questions
Is recovered solvent quality comparable to virgin solvent?
Typically, yes. Independent testing consistently shows properly distilled solvent meets or exceeds purity standards for most industrial processes. In critical applications like pharmaceutical formulation, small virgin solvent additions ensure specifications while maintaining significant savings.
Can mixed solvents be recycled together effectively?
Depends on boiling points and compatibility. Solvents with similar boiling ranges can sometimes yield usable blends. When components have significantly different boiling points or form azeotropes, separate distillation is recommended. Laboratory testing with actual samples provides definitive feasibility confirmation.
Is Solvent Recovery Right For You?
A solvent recovery distillation unit delivers maximum value when:
Solvent purchasing and disposal costs are significant
Your facility has consistent organic solvent waste streams
Environmental compliance initiatives seek waste reduction
Space and electrical infrastructure allow equipment installation
With 90-95% recovery efficiency, most facilities transition from the traditional linear "buy-use-dispose" model to a financially and environmentally superior closed-loop solvent cycle.
